10 year ascvd risk calculator aha
For primary prevention statin therapy should lower LDL-C approximately 30 to less than 50 with a moderate-intensity statin and greater than or equal to 50 with. These cardiovascular risk assessments use personal health information to calculate a 10-year and lifelong risk of heart disease.

Estimating Your Risk Of Heart Attack And Stroke There S An App For That The Skeptical Cardiologist
Low-risk.
. The online AHA Cardiovascular CV Risk Calculator is a modified ASCVD Risk Calculator that asks fewer questions. This calculator is for use only in adult patients without known ASCVD and LDL 70-189 mgdL 181-490 mmolL. The ACCAHA guidelines and the JBS3 guidelines both discuss consideration of lifetime risk as well as 10-year risk for cardiovascular events and JBS3 recommends use of the QRISK lifetime CV risk calculator in patients at low 10-year risk.
If you have generally it is recommended that you discuss with your doctor about starting aspirin and a statin. 1 Patients are considered to be at elevated risk if the Pooled Cohort Equations predicted risk is. For more information about the inputs and calculations used in this app see Terms and Concepts in the Resources tab below.
10-year risk of heart disease or stroke. Secondary non-lacunar stroke prevention in antihypertensive drug naïve patients is the only high-risk co-morbidity for which the 14090 mm Hg treatment initiation threshold is recommended. Our ASCVD Risk Algorithm is a step-wise approach for all adult patients including those with known ASCVD.
The updated 10-year ASCVD risk at follow-up visits and projected 10 -year ASCVD risk values are derived from. In adults with diabetes and 10-year ASCVD risk 20 it may be reasonable to add ezetimibe to maximum tolerated statin therapy to reduce LDL-C by 50. In patients with coronary artery disease or whose risk of ASCVD is 10.
Determines 10-year risk of heart disease or stroke and provides statin recommendations. 10-year risk for ASCVD is categorized as. 1 Patients are considered to be at elevated risk if the Pooled Cohort Equations predicted risk is.
Cardiovascular risk assessment in adults 10-year ACCAHA 2013 conventional and SI units Close. This calculator includes inputs based on race which may or may not provide better estimates so we have decided to make race optional. The long-anticipated release of the 2018 American College of CardiologyAmerican Heart Association cholesterol guidelines is now at hand and likely to be met with broad interest by clinicians in multiple specialties.
Also incorporates JNC-8 blood pressure guidelines and USPSTF aspirin prescribing guidelines. Providers also use the ASCVD Risk Calculator to see. Low-risk.
In such patients a blood pressure target of. This calculator helps health care providers to estimate 10-year risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease ASCVD defined as coronary death or nonfatal myocardial infarction or fatal or nonfatal stroke based on the Pooled Cohort Equations. Low-risk.
This peer-reviewed online calculator uses the Pooled Cohort Equations to estimate the 10-year primary risk of ASCVD atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among patients without pre-existing cardiovascular disease who are between 40 and 79 years of age. 1 persons with clinical ASCVD ie acute coronary syndromes or a history of myocardial infarction. 57 2022 Pre-Sessions Symposia Early Career Day.
On the basis of your calculated risk for heart disease or stroke under 10 the USPSTF guidelines suggest you would. Calculates ASCVD risk for heart disease and stroke using the 2013 ACCAHA guidelines. Patients with low absolute cardiovascular risk 10-year ASCVD risk.
Cardiovascular risk assessment in adults 10-year ACCAHA 2013 conventional and SI units. For more information about the inputs and calculations used in this app see Terms and Concepts in the Resources tab below. To continue reading this article you must log in with your personal hospital or group practice subscription.
It can be considered for patients aged 40 to 59 whose 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease exceeds 10 but absolute benefit is likely to be small. In adults with diabetes older than 75 years after a patient discussion of potential benefits and risks it may be reasonable to initiate statin therapy. This calculator assumes that you have not had a prior heart attack or stroke.
The risk is categorized as follows. Calculate your 10-year risk of heart disease or stroke using the ASCVD algorithm published in 2013 ACCAHA Guideline on the Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk. 1 The last update to the American College of CardiologyAmerican Heart Association cholesterol guidelines in 2013 takes a much narrower.
Informal calculation of lifetime risk of ASCVD for persons. 10-year risk for ASCVD is categorized as. This peer-reviewed online calculator uses the Pooled Cohort Equations to estimate the 10-year primary risk of ASCVD atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among patients without pre-existing cardiovascular disease who are between 40 and 79 years of age.
Estimate 10-year risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The on-treatment BP target is however. 2013 ASCVD Risk Calculator.
The ASCVD Risk Assessment Calculator gives both the 10-year and lifetime risk of developing atherosclerotic heart disease which includes heart attack and stroke. In adults with diabetes and 10-year ASCVD risk 20 it may be reasonable to add ezetimibe to maximum tolerated statin therapy to reduce LDL-C by 50. Still your results should be nearly identical.
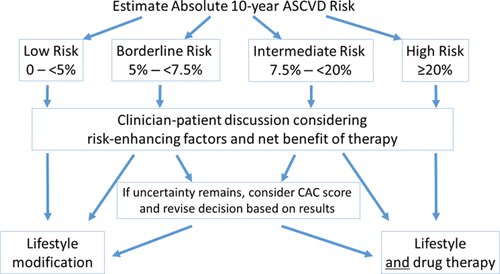
Less than 5 low risk 5 to less than 75 borderline risk 75 to less than 20 intermediate risk Greater than or equal to 20 high risk. This updated guideline focuses on reducing the risk of ASCVD in four statin benefit groups. The clinician-patient discussion should be undertaken to discuss the introduction of high or moderate-intensity statin in situations such as less than 5 to 75 10-year ASCVD risk.
The Work Group notes that this ACCAHA COR IIb recommendation is consistent with the recommendations in the 2010 ACCFAHA guideline 43 for patients with a 10-year CHD risk of. In adults with diabetes older than 75 years after a patient discussion of potential benefits and risks it may be reasonable to initiate statin therapy. Framingham Risk Score Hard Coronary Heart Disease.
Initial 10-year ASCVD risk either at a first visit or a previous visit being used for comparison is calculated via the Pooled Cohort Equation published as part of the 2013 ACCAHA Guideline on the Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk. For more information about the inputs and calculations used in this app see Terms and Concepts in the Resources tab below. The risk calculator is based on sex age race total and high-density lipoprotein.
10-year risk for ASCVD is categorized as.
2

2019 Acc Aha Guideline On The Primary Prevention Of Cardiovascular Disease A Report Of The American College Of Cardiology American Heart Association Task Force On Clinical Practice Guidelines Circulation

New Web Based 10 Year Ascvd Risk Calculator Pooled Cohort Equations Clincalc Com

Ascvd Risk Estimator
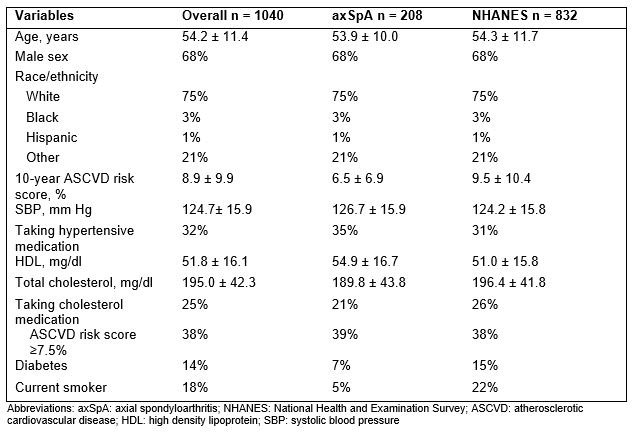
Ten Year Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Scores In Axial Spondyloarthritis Versus The General Population A Cross Sectional Study Acr Meeting Abstracts
Ascvd Risk Estimator
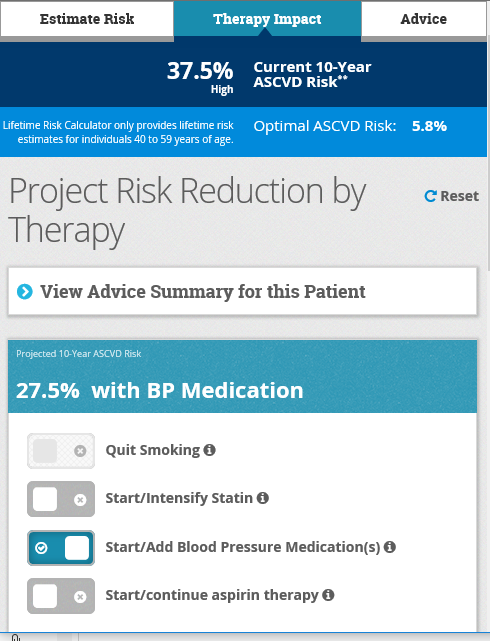
Ascvd Risk Estimator Plus American College Of Cardiology
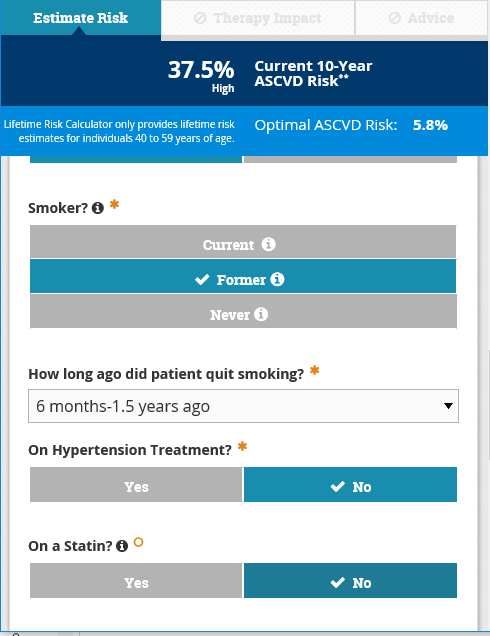
Ascvd Risk Estimator Plus American College Of Cardiology
تويتر Dr Deepak Krishnamurthy على تويتر Discuss Your Ascvd Risk Score With Your Doctor It Can Be Calculated With An Online Calculator And Treatment Recommended Based On The Score Https T Co Ypztu44n6q
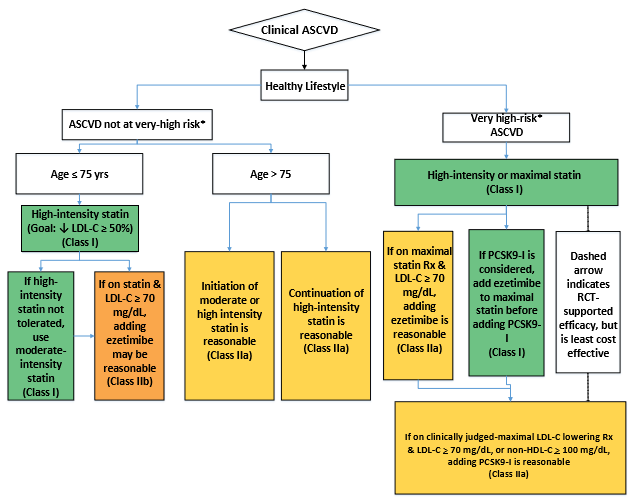
Ascvd Risk Estimator

Ascvd Risk Estimator
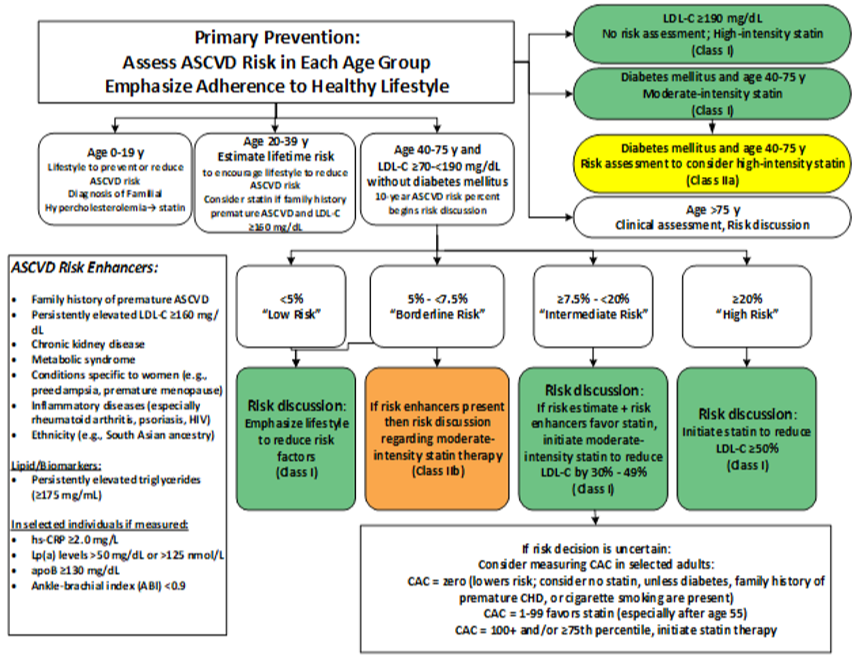
Ascvd Risk Estimator

Cardiovascular Risk Estimation By The Ascvd Risk Estimator Application In A University Hospital International Journal Of Cardiovascular Sciences
Ascvd Risk Calculator
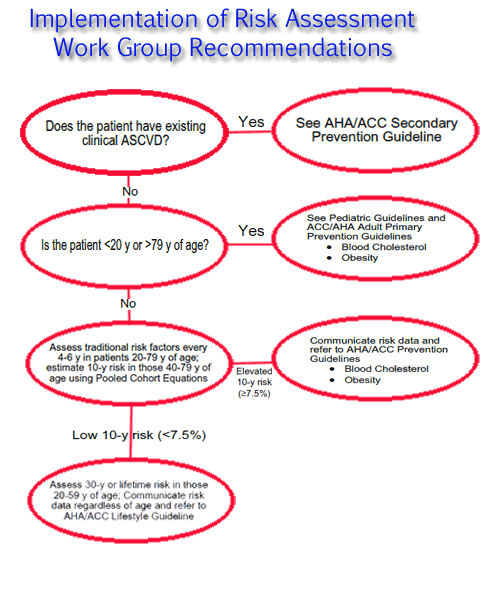
Atp Iv Lifetime Ascvd Risk Pooled Cohort Equations Globalrph

Ascvd Risk Estimator

Rapidascvd Calculate Ascvd Scores Seriously Fast Clincalc Com